Wed 22 Jun 2016
The Night Marchers of Kaua’i
Posted by PJ under developers, fairies, folklore, hauntings, spirits, taboo
No Comments
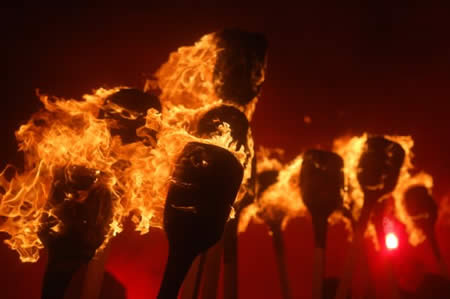
The purpose of this post is mostly to call attention to this fascinating and readable academic article by Katharine Luomala from Pacific Studies, 1983. Ms. Luomala does a thorough—and nonjudgmental—investigation of the widely perceived phenomena of Night Marchers, torch-bearing spirit processions which are still being perceived today in the Hawaiian islands. These processions seem to share similarities with the trooping fairies of Ireland, as well as other marching “beings.†There may also be something of the Wild Hunt in this mythology, as well.
The Night Marchers, however, are distinctly Hawaiian, incorporating in their processions the ritual of taboo, where it was on pain of death that ordinary people looked upon the being of sacred chiefs.
As Ms. Luomala explains:
The most sacred chiefs and chiefesses were carried in litters because their feet would taboo the ground. They seldom went out except at night, thus preventing the disruption of daily labor and the chance of a polluting shadow falling on anything or anybody. A taboo-breaker might be killed or seized for a sacrifice at a high chief’s heiau (place of worship). Sometimes the penalty was extended to the violator’s entire family group.
Even in spiritual form, it is widely believed, if you look upon the Night March, you will die—or be kidnapped and forced to march with them for eternity. Whenever you see a line of torches flickering in the distance and dark, folk of the islands say it is best to run as fast in the opposite direction as you can. If flight isn’t possible, hide—but by all means, do not do any curious peeking from your hiding place or you are doomed. If even hiding is not possible, prostrate yourself on your face on the ground and do not look up until you have heard the sound of marching feet pass you by and disappear in the distance.
Here’s the testimony of a limpet picker from 1970:
Suddenly I heard the sound of a conch shell blowing in the distance. Keoki heard it too. I thought it was the wind. Then a little while later we heard it again. This time it was a little louder. It was spooky because we didn’t see anything. Then we heard it again. We looked toward Ka-wai-hae side and then we saw it. It looked like a procession. At first we saw a line of torches in the distance. The procession was moving along the coastline. The conch shell blew again.
I took out my knife and Keoki got the rifle. We went seaward and laid down on the lava rock. We knew about night marchers from other fishermen. We knew you aren’t supposed to look upon the marchers and to lay on the ground face down. We did this. The marchers passed about fifty yards in front of us on the sand path. As they passed we could hear the sound of a drum pounding beat by beat. We didn’t look up until they were farther down the coast. All we could see now was the line of torches, and all we could hear was the far away sound of the conch shell. We didn’t know if they were going to come back that night, but we didn’t want to stick around and see.
Ms. Luomala recounts many such reports—from native islanders, tourists, European explorers—and places them within the context of Hawaiian belief. Like I said, a fascinating article.
I shouldn’t confess this, but I have a terrible addiction to junk TV. I saw a recent episode of Ghost Asylum, one of the stupider ghost hunter shows on the air. They did an investigation of the abandoned Coco Palms resort, reportedly built over one of the well-known pathways of the Night Marchers of Kaua’i. Many locals believe the resort was cursed from the start and is badly haunted. They won’t go there after dark, and say Night Marches are common on the property. It was destroyed by Hurrican Iniki in 1992 and never rebuilt. Some locals say this was a curse visited on them for the sacrilege of building on sacred land. But…developers are currently planning to tear down the Coco Palms and rebuild a new, grander resort. This would bring much needed jobs to the island, but local sentiment is mixed. It’s not for me to say whether development on a sacred site is a wise plan or just more developer hubris, but the investors have pledged to respect the land. They also brought in a shaman to do a blessing, just in case.




